Value Fluctuation Chart
Overview
The 'Value Fluctuation Chart' Lightning Web Component (LWC) provides a clear and effective visualization tool for displaying comparative data within Salesforce. This component is designed to represent data in a format that allows users to easily compare metrics over different time periods. By leveraging the Value Fluctuation Chart, users can quickly assess performance fluctuations, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
How Does It Work?
The Value Fluctuation Chart displays data in a comparative format, highlighting fluctuations between different time periods. The chart includes:
- Actual Value: The current value of the metric for the specified period.
- Previous Value: The value of the metric from a previous period, used for comparison.
- Title (Optional): A specific title for the chart, providing context to the data being displayed.
- Fluctuation Details (Optional): Additional context or details about the fluctuation being displayed.
- Format Pipe (Optional): A function to customize the format of the displayed values (e.g., currency formatting).
Usage
Setting Up the Flow
To use the Value Fluctuation Chart, you need to set up a flow in Salesforce that retrieves the necessary data and passes it to the LWC. Here’s how you can do it:
Define the
ResultCollectionVariable:- In the Flow Builder, create a new variable named
ResultCollection. - Set the Data Type to
Text. - Ensure "Allow multiple values (collection)" is checked.
- Mark it as "Available for output" so it can be accessed by the component.
- In the Flow Builder, create a new variable named
Create a Formula Resource:
- Create a new resource of type
Formula. - Set the API Name to something like
LaFormula. - Set the Data Type to
Text. - Use the formula editor to construct your JSON string. For example:
'{"actualValue": "' + TEXT(5) + '", "previousValue": "' + TEXT(10) + '", "title": "Test"}' - This formula constructs a JSON string with the specified values.
- Create a new resource of type
Assign the Formula to
ResultCollection:- Add an
Assignmentelement to your Flow. - Set the
ResultCollectionvariable to the value of the formula resource (LaFormula). - Ensure the operator is set to
Add.
- Add an
Save and Activate the Flow:
- Save your Flow.
- Activate the Flow if it's not already active.
Using Input Queries
Alternatively, you can use input queries to provide data to the Value Fluctuation Chart. Here’s how:
Define Input Queries:
- Create a list of input queries as a JSON string. Each query should include a key (reference ID) and a value (SOQL query).
- Example:
[
{"referenceId": "opportunities", "query": "SELECT Id, Amount, CloseDate FROM Opportunity WHERE IsWon = true AND CloseDate != null"}
]
Pass Input Queries to the Component:
- Use the
inputQueriesattribute of the Value Fluctuation Chart component to pass the JSON string of input queries. - The component will execute this query and use the results to populate the chart.
- Use the
Create a Transformation Function:
Define a JavaScript transformation function in a file and upload it as a Static Resource in Salesforce. This function will process the query results and format them for the Value Fluctuation Chart.
Example:
/* All functions should be defined within the window.MobeeDynamicFunctions scope in order to work with the Mobee mobile App */
window.MobeeDynamicFunctions = {
opportunityFluctuation: (inputData) => {
let opportunities = inputData['opportunities'];
const result = [];
let opportunitiesWithYear = opportunities.map((item) => {
let dateYear = '';
if (item.CloseDate) {
dateYear = new Date(item.CloseDate).getFullYear();
}
let resultItem = { ...item };
resultItem.CloseDateYear = dateYear;
return resultItem;
});
const groupBy = (xs, key) => {
return xs.reduce(function (rv, x) {
(rv[x[key]] = rv[x[key]] || []).push(x);
return rv;
}, {});
};
let groupedData = groupBy(opportunitiesWithYear, 'CloseDateYear');
let sumPreviousYear = 0;
let currentYear = new Date().getFullYear() - 1;
let previousYear = currentYear - 1;
if (groupedData[currentYear]) {
sumPreviousYear = groupedData[previousYear]
.map((item) => item.Amount || 0)
.reduce((previousValue, currentValue) => previousValue + currentValue, 0);
}
let sumCurrentYear = 0;
if (groupedData[currentYear]) {
sumCurrentYear = groupedData[currentYear]
.map((item) => item.Amount || 0)
.reduce((previousValue, currentValue) => previousValue + currentValue, 0);
}
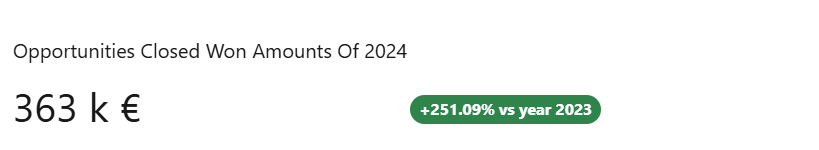
result.push({
actualValue: sumCurrentYear,
previousValue: sumPreviousYear,
title: 'Opportunities Closed Won Amounts Of ' + currentYear,
fluctuationDetails: 'vs year ' + previousYear,
formatPipe: (actualValue) => {
return new Intl.NumberFormat('fr-FR', {
style: 'currency',
currency: 'EUR',
notation: 'compact',
}).format(actualValue);
},
});
return result;
}
}
Upload the JavaScript File as a Static Resource:
- In Salesforce, navigate to Setup.
- In the Quick Find box, type Static Resources and select Static Resources.
- Click New to upload your JavaScript file containing the transformation function.
- Provide a name for the Static Resource (e.g.,
MyMobeeFunctions) and upload the file.
Set the Transformation Function:
- In Mobee Settings, set the
Mobee Dynamic Function File Nameto the name of the Static Resource you created (e.g.,MyMobeeFunctions). - In the field labeled JavaScript Transformation Function Name, enter the name of the function you defined (e.g.,
opportunityFluctuation).
- In Mobee Settings, set the